TDC teaches how to deliver a vibrant interactive experience
How does a conference make the transition to virtual participation in the age of the COVID-19 virus? And suppose you have less than two months to do so?
As social distancing loomed as a dire necessity in February and March 2020, many organizations simply threw up their hands and canceled their conferences. But some were prepared to put their offering online. The major Brazilian organization “The Developer’s Conference” is particularly worth examining for their online work. Building on previous experiences with hybrid conferences (mixed on-site and online), they rethought everything about what they were doing and produced a unique experience that they are now teaching others to reproduce.
The amount of interaction among speakers, sponsors, and attendees at TCDOnline was a much as ever, perhaps more so. And the 30 staff gracefully handled 6,750 attendees.
This article, based on a conversation I had with event director Yara Senger, will show how they did it.
TDC started in 2007. As early as 2009, they offered a cost-free online component along with their regular on-site conference. But the online component was modest: just video feeds of the speakers. Attendance was growing gradually over the years, and toward the end was about 11,000 on-site attendees with an additional 5,000 to 6,000 online participants.
Organizers could tell that there was not much interaction by online participants. In particular, the online participants offered little benefit to sponsors, whose satisfaction is crucial to make conferences work financially. If they just extended this format to an all-virtual conference, the experience would not be particularly positive. They worked from the premise that people need to feel comfortable with every aspect of an online experience in order to attract them year after year.
So the organizers started from the ground up, producing a very different kind of conference. Some of the important changes follow.
- The traditional experience of being greeted when you enter the door of an event was reproduced by banks of employees who approached every attendee as they logged into the conference. Every question received a prompt answer. If someone couldn’t get into a room for some technical reason, they could get help in a chat.
- Video was available, so that you could see the people you were talking to. I asked Senger whether bandwidth was a problem, because I assumed that many areas of Brazil would be poorly provisioned with network connections. She said that the organizers heard only a few complaints, and that bandwidth was not an issue. This is a tribute, I think, to the brilliant engineering that developers have put into designing and implementing streaming protocols.
- Many parallel activities were offered on virtual streams that the organizers called “rooms.” Thus, there would be a room for each track, where people could stay for multiple sessions.
Tracks, I should explain, form the basic structure of TDC. Typical tracks in 2020 included Agile, Agile for business, Artificial Intelligence and data, programming language, etc.—the kinds of topics that are popular at all computer conferences today. Attendees pay separately for each track they want to attend.
Some sponsors also rented “rooms” to offer demos and other content. Registration and questions were also handled in a dedicated room.
- If participants wanted to connect with a speaker after a talk, they could leave the track’s room and visit a separate room for informal discussion. These went very well, showing that some 200 people could interact in an orderly fashion online. Some of the sessions went on until 11:00 at night, with perhaps 20 stalwart attendees lasting the whole time.
Senger said that interactions in the rooms were probably more formal than face-to-face meetings, which is a drawback of virtual meetings. But they allowed many more people to participate for a longer time than when sessions are on-site.
- Participants could network with each other in a serendipitous way, a little like hallway chats at face-to-face conferences. At TDCOnline, you could enter a room with another randomly chosen participant and introduce yourselves to each other for three minutes.
- Participants could transition between rooms with a single click. This is one of the advantages of the software used by TDC to administer the conference, Hopin. Hopin was available at a reasonable price and offered important features TDC needed. It let them set up separate tracks (one per room, as said before) and set participants’ permissions so they had access only to the tracks they paid for.
- Session monitors followed the presentations in real-time and put resources up quickly in chat boxes. When a speaker mentioned a resource such as room to move it, the monitor could post a link to the resource within a couple seconds. They were so effective that some participants assumed that an NLP-powered chatbot was doing it.
- Each track during the on-site conference used to continue for eight hours, and people were encouraged to stay for the whole day. (They were always charged for the entire track.) Organizers realized that eight hours of conferencing online would grueling–even if some participants were delighted to stay till 11:00 at night–so tracks were reduced to four hours.
- Along with the reduction in the length of a track, sessions were reduced to 25 minutes each. This shifted much of the discussion from the formal session to the informal follow-up. And this, in turn, allowed the discussion to reflect better the interests of the attendees.
- There were also more panels than in previous years. The debates there were lively and productive, according to Senger. Some panels went on for three hours. Attendees could submit questions and vote on the questions submitted by others, so the most popular questions got plenty of attention.
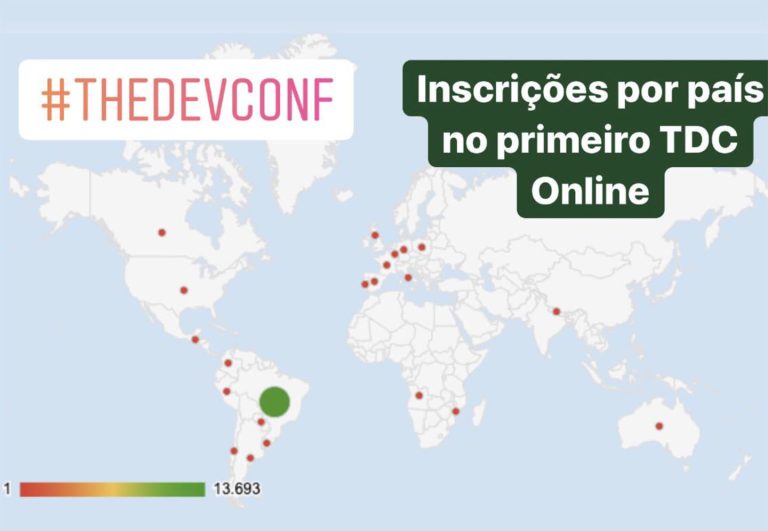
What was the payoff for all this insight and planning? The conference ultimately drew a respectable number of 6,750 attendees, who logged in from every region of Brazil—bringing much broader participation geographically than ever before—and included people from 21 other countries too. (These countries are marked by red dots in the article image) Remember that the sessions were all in Portuguese, so this reveals a thriving international community of Brazilians and other people fluent in Portuguese. About 15 sponsors participated. A sparkling, fast-paced video conveys some of the experience.
I asked whether different types of people came this year, because it was online. Except for the great geographic spread, Senger said people seemed to be basically like the ones who came to earlier TDCs. The only difference is a slight decrease in experience levels. Only 39% of attendees had ten or more years of experience in their fields, compared to an average of 44% before. But there was a big increase among the great with 6-10 years of experience. This is understandable, because the conference was four times as large this year. There are a lot more people with 6-10 years of experience than with ten years.
As you can probably tell from my description of the conference, it depended heavily on the responsiveness and expertise of the staff. I asked Senger how they could handle 6,750 with only 30 staff, and she answered that the staff are well-trained and have been running their conferences for years. The speakers need a great deal of support, starting by testing their connections two weeks before the conference, ensuring they were ready the day before, and setting up their session right before it started.
I also asked how easily attendees picked up the rules for attendance. Senger said that it required a lot of explanation. The organizers are preparing a video that attendees can view before future conferences to grasp what they can do to make their participation as effective as possible.
TCDOnline was successful because of the unique structure and tools provided to speakers, sponsors, and attendees. The organizers are now consulting with other organizations to teach the lessons of the first TCDOnline and help others produce engaging and educational conferences during this period of physical distancing—and perhaps even after that period has ended.
